Virtual Research Environment
Last updated on 2024-12-31 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 12 minutes
To enable collaboration and open access as well as open science practices, it is recommended to manage the multidimensional media in a way which is accessible to the team you are working with and with others who might benefit from the effort you have done to curate the data.
There are some web-platforms which can easily allow this, such as document management and storage system, e.g.
All these enable sharing capabilities with people within and beyond your organisations.
Other systems such as Virtual Research Environments are also available for sharing data with the same community of practice.
Virtual Research Environments (VRE)
VREs make it easy for teams across organisations to collaborate in data-driven research process. We will use D4Science in this lesson.
For example, a project that you are developing with friends/colleagues might involve investigating how it was living in Brighton in the 18th century. You might be using this to recreate visually a scene in the city.
Visual information can make it easier to develop the project, and it can also be more engaging for users to feedback on early prototypes.
Information can include:
- Mapping the geographical areas which were inhabited in Brighton as well as any roads.
- What architecture did larger and smaller buildings had?
- How did people dress?
- What activities they did?
To enable collaboration and support FAIR principles, Virtual Research Environments (VRE) can be useful. VREs are collaborative environments created on-demand allowing remote sharing of applications, services and data resources.
We will make use of D4Science to explore further these environments.
Either click on the link or copy/paste to your browser the address: https://services.d4science.org/group/d4science-services-gateway/explore.
Login by using your existing login credentials, e.g. the one of your institution or your Google account.
You will see the main interface upon successful login. See below.
The VRE offers the following capabilities:
- Workspace: enables members to store and share data securely.
- Mailing System and Forum: enable members to community one-to-one or as a community.
- Data Analytics: enable members to access cloud computing facilities to collaborate in developing and applying data-algorithms.
To test some of these access in the main interface, the menu bar at the top showing the Workspace and an Analytics menu items. Click on any of them to access this functionality.
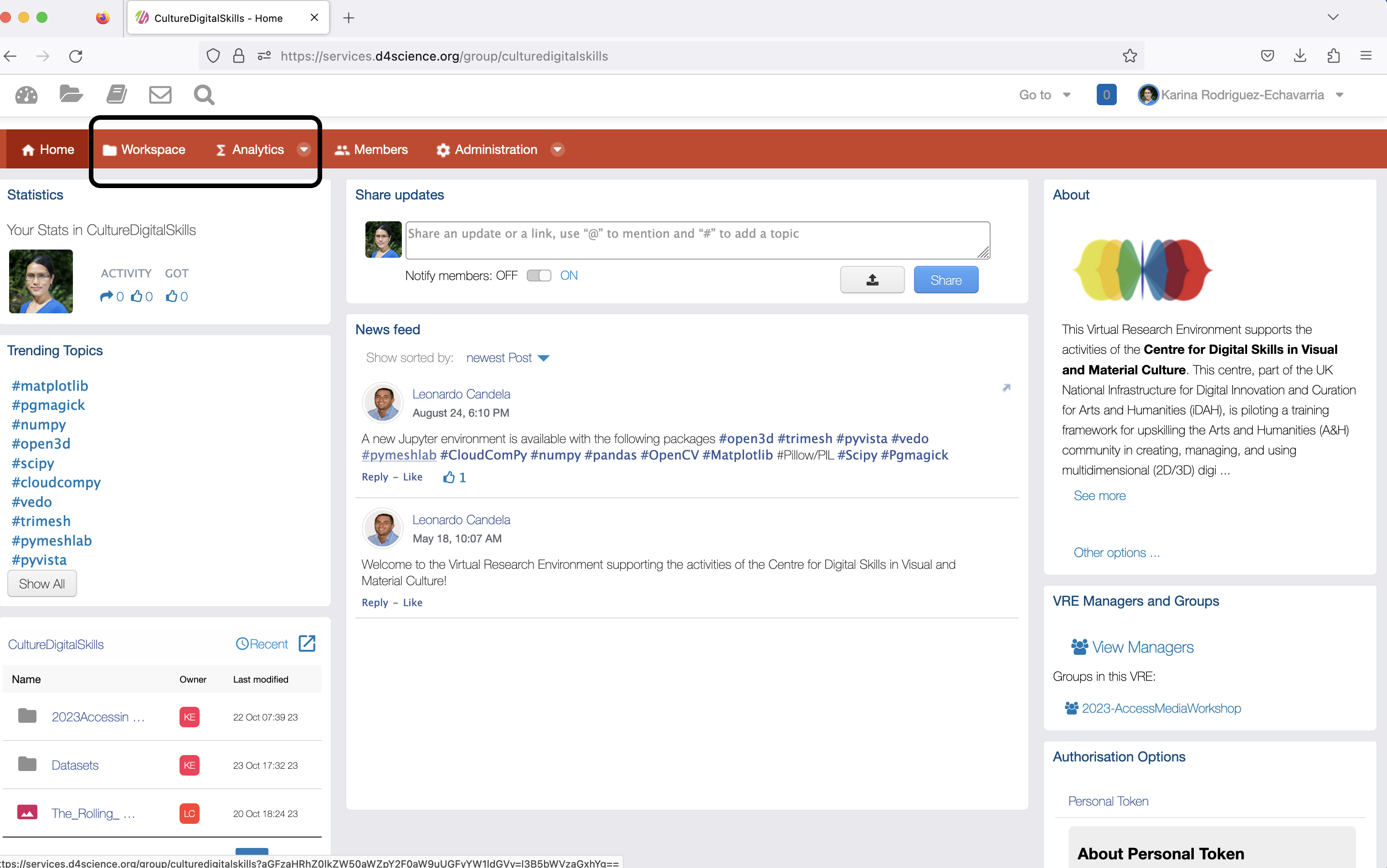
Click on Workspace.
Workspace
The workspace allows a member to create and share folder, as well as upload files.
It facilitates on-line file sharing across organisations.
Folders and data can be shared with all or specific users of the VRE.
Testing the Workspace: Upload a file
Using what you have learned on downloading media, access an example of an image from a repository from your institution or a project.
If you don’t have any, use the following from Wikimedia:

Create a folder in your workspace, upload the image and share with another person in the group.
The functionality that the workspace provides include:
- Preview the file.
- Get basic information - note that vary basic metadata, such as name, ID, and type are supported. There is a description field which allows for recording additional metadata.
- Version number, as the owner of a file can replace the file keeping the older versions to facilitate version control.
- Searchable link to the file.
- History of operations performed by users to the file.
- Move to another folder.
- Make a copy to another folder.
- Rename and Delete the files.
- Show and Download to the local computer.
VRE Analytics
VREs also provide access to an interactive development environment for Notebooks, code, and data. For this, the VRE provides access to a JupyterLab enviornment. It supports over 40 programming languages, including Python, Java, R, Julia, and Scala.
The Notebooks environment are increasingly used by researchers where they can combine text, mathematics, computations and rich media output. It requires of a special language for formatting text known as markup.
The environment also support basic editing of text-data and the implementation of data processing algorithms using high-performance back end computers.
Challenge
Access JupyterLab in the Analytics menu. Select one of the options for accessing a virtual server.
This will create a ‘virtual’ machine.
You should find a Navigate to the folder where you created by clicking on the folder icon on the left menu.
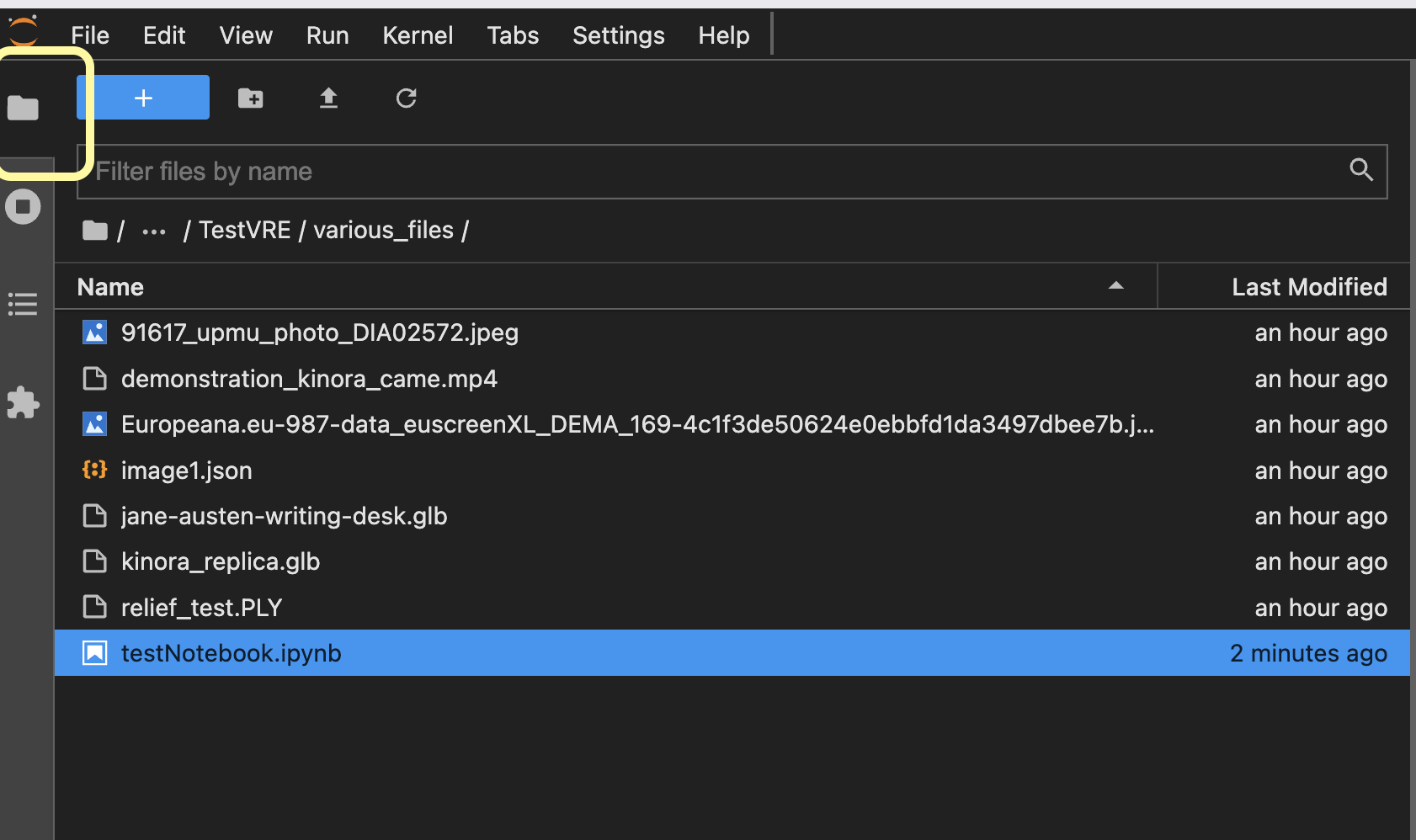
Create a new Text file, by clicking on the + icon, and selecting Other -> Text File.
Change its name and save it.
Key Points
Multidimensional media requires good management, to underpin collaboration and open access/science processes.
Virtual Research Environments (VREs) are collaborative spaces for data-driven research.
VREs offer workspaces for secure data storage, mailing systems, forums, and data analytics capabilities.
