Content from Introduction
Last updated on 2024-12-31 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- How does copyright law affect the use of multidimensional dataset?
Objectives
- To understand copyright law in the UK.
- To be aware of the impact of the copyright legislation on personal practice for collecting multidimensional data.
- Demonstrate that this understanding can be applied on a dataset.
This lesson presents information that has been gathered from a mixture of web resources, references and links:
- British library: https://www.bl.uk/business-and-ip-centre/articles/what-is-copyright
- Jisc guides: https://www.jisc.ac.uk/full-guide/copyright-law
- Jisc digitisation:https://www.jisc.ac.uk/guides/3d-digitisation-and-intellectual-property-rights
-
Gov.uk:
- General copyright information https://www.gov.uk/copyright
- Copyright specific to images: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/copyright-notice-digital-images-photographs-and-the-internet/copyright-notice-digital-images-photographs-and-the-internet
-
Creative Commons (CC):
- Licenses: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/
- License chooser: https://chooser-beta.creativecommons.org/
- Creative Commons Corporation (2011), The Power of Open, https://thepowerofopen.org/assets/pdfs/tpoo_eng.pdf
- Pila, Justine, Copyright and its Categories of Original Works (July 1, 2008). Oxford Journal of Legal Studies, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 229–254, 2010, Oxford Legal Studies Research Paper No. 22/2008, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1160176 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1160176
- Wallace, Andrea. A Culture of Copyright: A scoping study on open access to digital cultural heritage collections in the UK. Research Report. Towards A National Collection, UKRI, (2022), https://openresearch.community/documents/a-culture-of-copyright-a-wallace
Content from Copyright Information
Last updated on 2024-12-31 | Edit this page
What is copyright?

Copyright is a legal right, which protects the copyright owner and/or the creator of a work.
Copyright gives the owner control over their work and how it is used.
There are four areas of intellectual property:
- Copyright: what the work is.
- Patents: how something works.
- Designs: what something looks like.
- Trademark: what you call it.
Works use the copyright symbol (©), a name and the year of creation.
Who owns the copyright?
 There is no
system in the UK for registering copyright.
There is no
system in the UK for registering copyright.
Authors automatically get copyright protection when the work is created.
Unless the work was created by an employee during their employment, or the copyright is transferred to someone else as part of their agreement.
What works does copyright protect?
There is no copyright protection for ideas/concepts.
Copyright only protects works when ideas are expressed in a form that can be reproduced or copied:
- Original literary, dramatic, musical and artistic work, including illustration and photography.
- Original non-literary written work, such as software, web content and databases.
- Sound and music recordings.
- Film and television recordings.
- Broadcasts.
- The layout of published editions of written, dramatic and musical works.
Multiple independent copyrights

The copyright in each type of work exists independently.
For example, a song may be covered by copyright:
- on the entire collection which contains the song.
- on the lyrics as a literary work.
- on the music of the song as its performance.
How copyright protects work
Copyright prevents people from:
- copying work
- putting someone’s work on the Internet.
-
distributing copies of someone’s work, whether free
of
charge or for sale
- renting or lending copies of someone’s work
- making an adaptation of someone’s work
- performing, showing or playing someone’s work in public
Exceptions
There are certain exceptions, especially in the case of photographs, films and recorded sound.
For example:
- making content accessible for disabled people.
- text and data mining for research.
- teaching, fair dealing and more.
See more information: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/exceptions-to-copyright#non-commercial-research-and-private-study
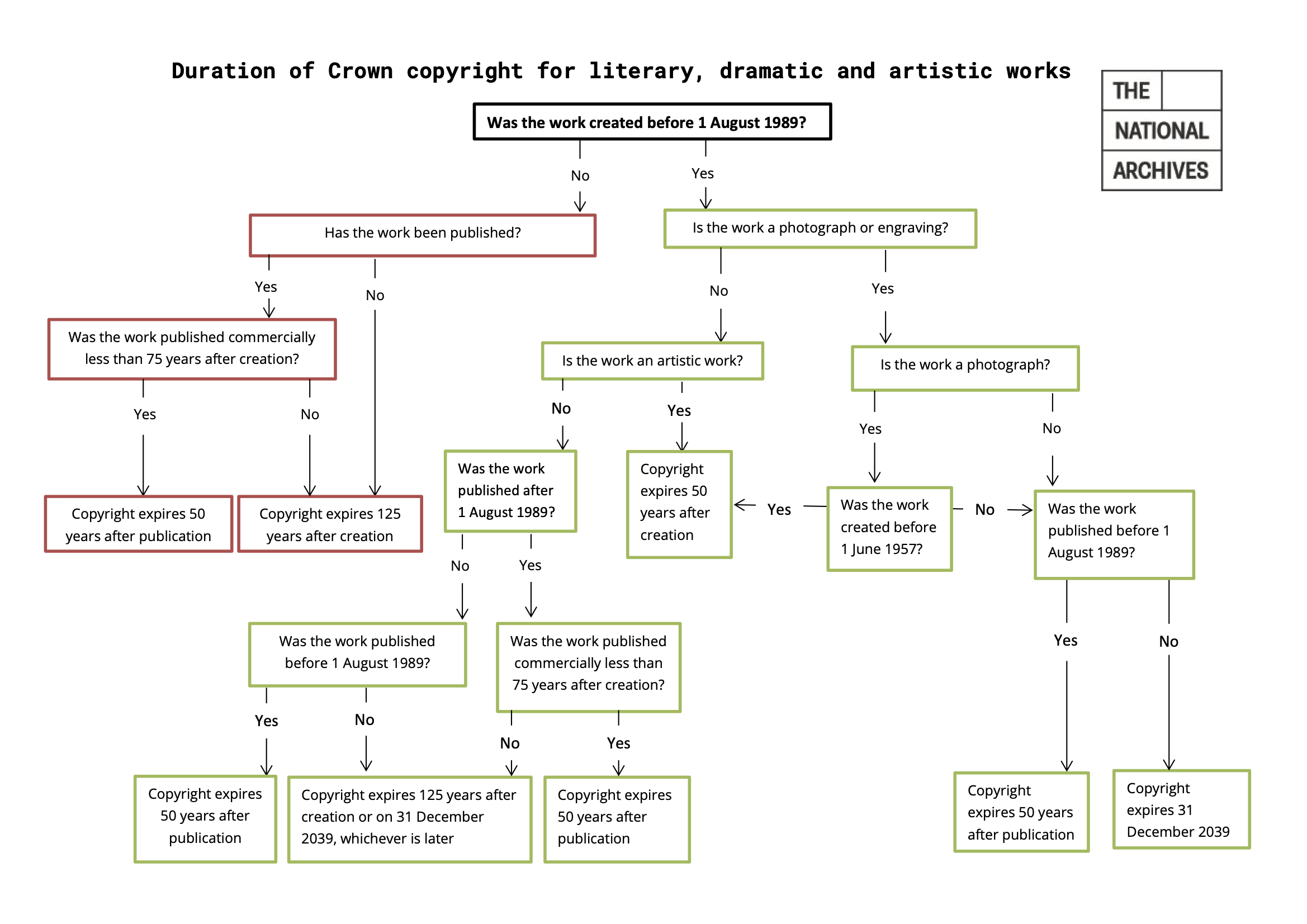
Copyright duration
Copyright protection starts as soon as a work is created.
After copyright expires, the work is in the public domain so anyone can use or copy the works.
| Type of work | How long copyright usually last |
|---|---|
| Written, dramatic, musical and artistic work | 70 years after the author’s death |
| Sound and music recording | 70 years from when it’s first published |
| Films | 70 years after the death of the director, screenplay author and composer |
| Broadcasts | 50 years from when it’s first broadcast |
| Layout of published editions of written, dramatic or musical works | 25 years from when it’s first published |
Source: https://www.gov.uk/copyright/how-long-copyright-lasts
Copyright owner: employees, freelancers and commissions
The copyright is an automatic right and does not need to be registered or paid for (by its owner).
The first owner of copyright will normally be the author (who created the work).
An employer is usually the first owner of copyright in work which is made in the course of an author’s employment under a contract.
For commissioned work and freelancers, the copyright usually lies with the person who creates the work unless it is specified in the contract. Hence, it is important when commissioning work to put an agreement in place first covering the intellectual property of the resulting work.
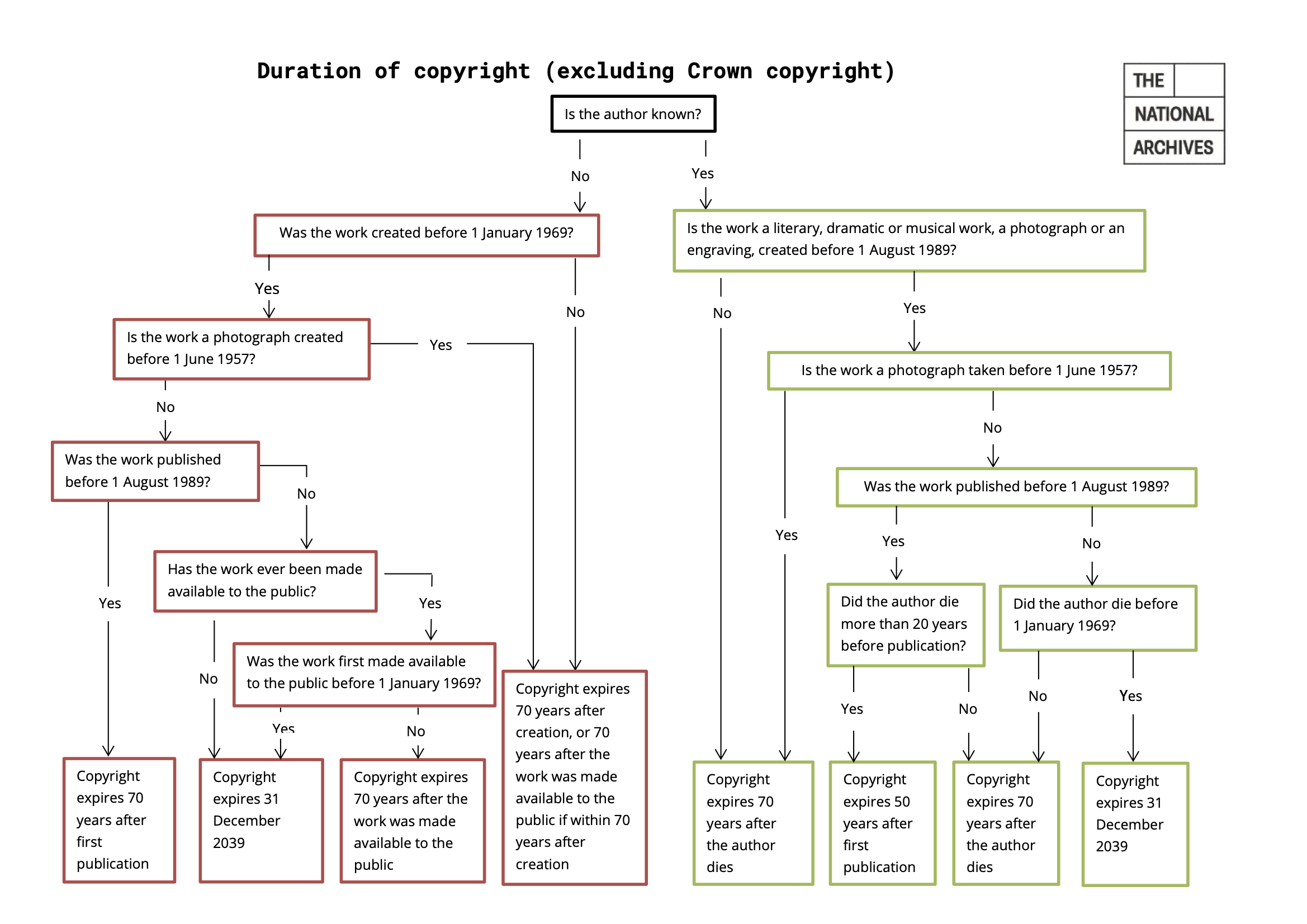
Copyright of Images in UK law
 Photographs, illustrations
and other images will generally be protected by copyright as
artistic works.
Photographs, illustrations
and other images will generally be protected by copyright as
artistic works.
The copyright owner of a photograph is its creator, for example, the photographer or the organisation/employer with which the photographer has a contractual agreement.
The creator of an image may choose to allow a person or organisation to license the work on their behalf, license the copyright directly themselves, or “assign” (transfer) the copyright to another person.
Copyright in images lasts for the life of the creator plus 70 years from the end of the calendar year of their death.
Hence, the length of the copyright period will depend on when the image was created.

Moreover, digital images covered by copyright protection include:
- Digital photos taken on mobile phones and digital cameras.
- Images that were first generated on photographic film and any digital images created from them.
- Images such as diagrams and illustrations.
Copyright resulting from digitisation works
Digitising, if understood as making a digital copy, is copying. This right is reserved to the copyright owner as we already established.
Creating a 2D digital image of a creative work, such as a painting, is unlikely to create new copyright in the digitised version.
There is some uncertainty regarding whether copyright can exist in digital images of older works (e.g. a painting or manuscript) for which copyright has expired. This is because the effort in the creation of the digital photograph is negligible.
New copyright will only arise in such digital copies if specialist skills have been used to optimise details (i.e. retouching images).
Uncertainty is due that according to established case law, copyright can only subsist in subject matter that is original in the sense that it is the author’s own ‘intellectual creation’.
Following this argument, there is potential for claiming copyright in a 3D digital image as a higher degree of skills goes into creating it.
Content from Licensing
Last updated on 2024-12-31 | Edit this page
Licensing copyrighted work
Licences are contractual agreements between the copyright owner/s and user/s limiting how the work can be used.
Examples of licences are:
- Jisc Model Licence
- Copyright owners can be represented by a collecting society who negotiates licenses with users, e.g. Spotify, CLA
- Creative Commons
Creative Works where a copyright owner is unknown or untraceable are known as Orphan Works. Guidance on how to deal with this cases is available from the UK government.
Creative Commons Licenses (CC)
Creative Commons licenses are a standardised way to grant copyright permissions to creative work by individuals, organisations and institutions.
They help creators to retain copyright while allowing others to copy, distribute, and make some uses of their work.
They are designed to be easy to use and understand by stating in simple terms what the user is allowed to do, and under which conditions.
They all have common features which serve as baseline. On top of which licensors can choose to grant additional permissions.

Why open cultural heritage data?
The Problem of the Yellow Milkmaid
‘The Milkmaid’, one of Johannes Vermeer’s most famous pieces, depicts a scene of a woman quietly pouring milk into a bowl. During a survey the Rijksmuseum discovered that there were over 10,000 copies of the image on the internet—mostly poor, yellowish reproductions. As a result of all of these low-quality copies on the web, according to the Rijksmuseum, “people simply didn’t believe the postcards in our museum shop were showing the original painting. This was the trigger for us to put high-resolution images of the original work with open metadata on the web ourselves. Opening up our data is our best defence against the ‘yellow Milkmaid’.”
Extract from Harry Verwayen, Martijn Arnoldus and Peter B. Kaufman (2011). The Problem of the Yellow Milkmaid: A Business Model Perspective on Open Metadata. (Acessed November 2023). URL: https://pro.europeana.eu/post/the-problem-of-the-yellow-milkmaid
Open Culture is an initative from Creative Commons.
It capitalises on the need to to empower creators anywhere in the world to discover, share, reuse and remix cultural heritage.
More information:
- Creative Commons for GLAMS: https://certificates.creativecommons.org/cccertedu/chapter/unit-5-creative-commons-for-glam/
- CC Needs and assessment report: https://creativecommons.org/2023/02/23/cc-needs-assessment-report-on-public-domain-tools-in-cultural-heritage-sector-unveils-key-insights/
Using copyrighted work
To use a creative work protected by copyright it is generally advised:
- Once you have found a creative work you would like to use, you will need to determine the type of usage:
- If it is not digitised, will you be producing a digital version?
- Would you like to remix/change it? if so, Are you willing to release the resulting creative work for further remixes?
- Would you be using it for commercial purposes?
- Understand the license which is currently offered with the creative work and its restrictions.
- If no license is available then find the owner of the copyright. Remember in many cases it might not be who holds the content.
- If you are using the creative work for educational purposes, confirm that your intended use falls within the exceptions to copyright.
- If you require a license, agree with the owner one. Favour the Creative Commons suite of licenses.
- Ensure you attribute the creative work when making use of it.
Content from Attributing works
Last updated on 2024-12-31 | Edit this page
It is important to reference creative works.
There are best practices when attributing works in order to recognise:
- Title of the work
- Copyright owner
- Source of the work
- License under which you use the work
For example:
“Still Life with Ham” by Pieter Claesz licensed under CC0

Challenge
For the data files you have curated, determine the copyright owner, and whether you are allowed to use the content for educational, non-commercial or commercial purposes.
Determine how to attribute the creative works.
